最长重复子串
方法一:二分查找 + $Rabin-Karp$ 字符串编码
分析
我们可以把这个问题分解成两个子问题:
从 1 到 N 中选取子串的长度 L;
检查字符串中是否存在长度为 L 的重复子串。
子任务一:二分查找
解决子问题一的最简单的方法是,我们从 L = N - 1 开始,依次递减选取子串的长度,并进行判断。如果发现存在长度为 L 的重复子串,就表示 L 是最长的可能长度。
但我们发现,如果字符串中存在长度为 L 的重复子串,那么一定存在长度为 L0 < L 的重复子串(选取长度为 L 的重复子串的某个长度为 L0 的子串即可),因此我们可以使用二分查找的方法,找到最大的 L。
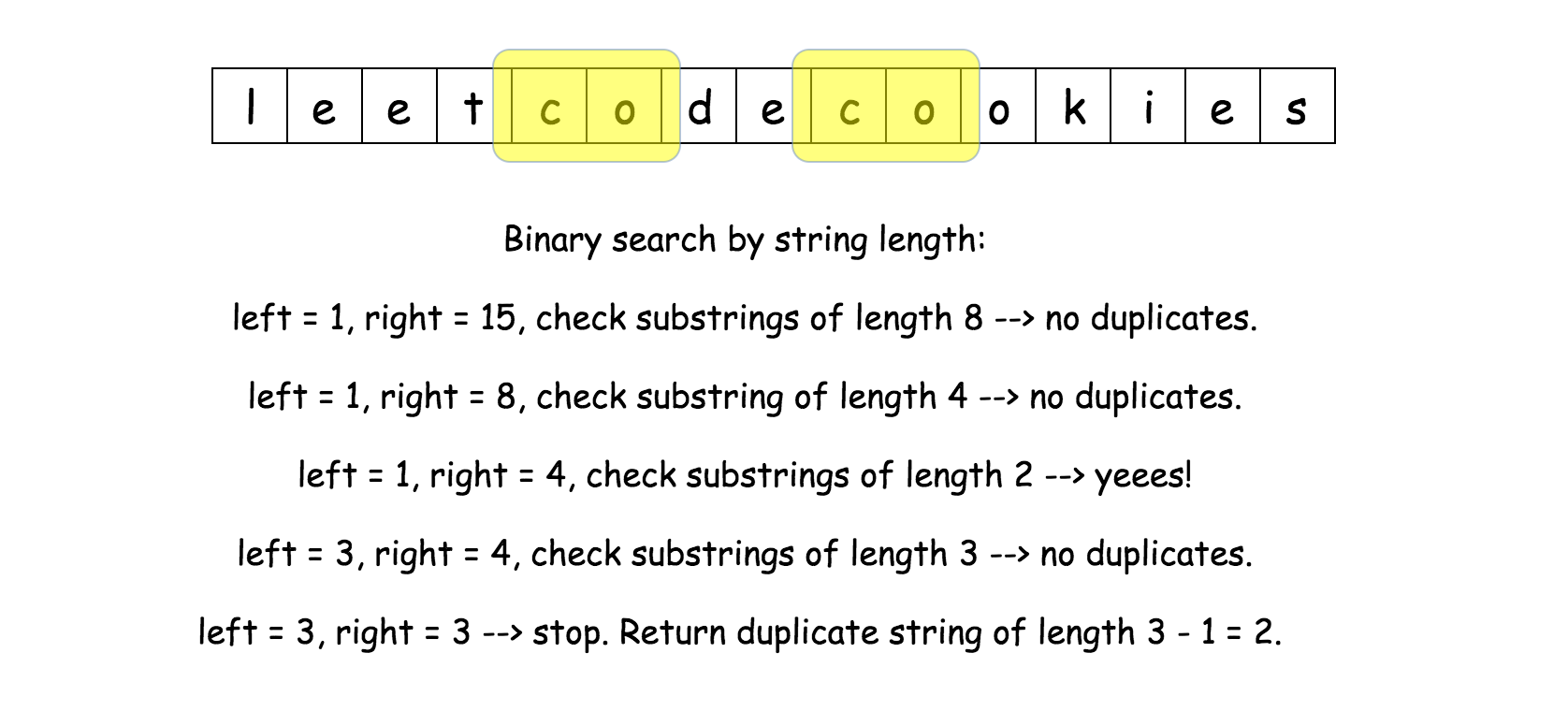
子任务二:Rabin-Karp 字符串编码
我们可以使用 $Rabin-Karp$ 算法将字符串进行编码,这样只要有两个编码相同,就说明存在重复子串。对于选取的长度 L:
- 使用长度为 L 的滑动窗口在长度为 N 的字符串上从左向右滑动;
检查当前处于滑动窗口中的子串的编码是否已经出现过(用一个集合存储已经出现过的编码);
- 若已经出现过,就说明找到了长度为 L 的重复子串;
- 若没有出现过,就把当前子串的编码加入到集合中。

可以看出,$Rabin-Karp$ 字符串编码的本质是对字符串进行哈希,将字符串之间的比较转化为编码之间的比较。接下来的问题是,在滑动窗口从左向右滑动时,如何快速计算出当前子串的编码呢?如果需要在 $O(L)$ 的时间内算出编码,这种方法就没有意义了,因为这个直接进行字符串比较需要的时间相同。
为了能够快速计算出字符串编码,我们可以将字符串看成一个 26 进制的数(因为字符串中仅包含小写字母),它对应的 10 进制的值就是字符串的编码值。首先将字符转换为 26 进制中的 0-25,即通过 $arr[i] = (int)S.charAt(i) - (int)'a'$,可以将字符串 $abcd$ 转换为 [0, 1, 2, 3],它对应的 10 进制值为:
$$h_{0} = 0 * 26^{3} + 1 * 26 ^{2} + 2 * 26 ^{1} + 3 * 26^{0} $$
我们将这个表达式写得更通用一些,设 $c_i$ 为字符串中第 $i$ 个字符对应的数字,$a = 26$ 为字符串的进制,那么有:
$$h_{0} = c_{0} a^{L-1} + c_{1} a^{L-2} + ... + c_{i} a^{L-1-i} + ... + c_{L-1}a^{1} + c_{L} a^{0}$$
$$= \sum_{i=0}^{L-1}c_{i}a^{L-1-i}$$
当我们向右移动滑动窗口时,例如从 $abcd$ 变成 $bcde$,此时字符串对应的值从 [0, 1, 2, 3] 变成 [1, 2, 3, 4],移除了最高位的 0,并且在最低位添加了 4,那么我们可以快速地计算出新的字符串的编码:
$$h_1 = (h_0 - 0 \times 26^3) \times 26 + 4 \times 26^0$$
更加通用的写法是:
$$h_1 = (h_0 a - c_0 a^L) + c_{L + 1}$$
这样,我们只需要 $O(L)$ 的时间复杂度计算出最左侧子串的编码,这个 $O(L)$ 和滑动窗口的循环是独立的。在滑动窗口向右滑动时,计算新的子串的编码的时间复杂度仅为 $O(1)$。
最后一个需要解决的问题是,在实际的编码计算中,$a^L$ 的值可能会非常大,在 $C++$ 和 $Java$ 语言中,会导致整数的上溢出。一般的解决方法时,对编码值进行取模,将编码控制在一定的范围内,防止溢出,即 $h = h \% modulus$。根据 生日悖论,模数一般需要和被编码的信息数量的平方根的数量级相同,在本题中,相同长度的子串的数量不会超过 $N$ 个,因此选取模数是 $2^{32}$ 无符号整型数的最大值)是足够的。在 $Java$ 中可以用如下的代码实现取模:
$$h = (h * a - nums[start - 1] * aL \% modulus + modulus) \% modulus;$$
$$h = (h + nums[start + L - 1]) \% modulus;$$
而在 $Python$ 中,整型数没有最大值,因此可以在运算的最后再取模:
$$h = (h * a - nums[start - 1] * aL + nums[start + L - 1]) \% modulus$$
在解决算法题时,我们只要判断两个编码是否相同,就表示它们对应的字符串是否相同。但在实际的应用场景中,会出现字符串不同但编码相同的情况,因此在实际场景中使用 $Rabin-Karp$ 字符串编码时,推荐在编码相同时再对字符串进行比较,防止出现错误。
Python
class Solution:
def search(self, L: int, a: int, modulus: int, n: int, nums: List[int]) -> str:
"""
Rabin-Karp with polynomial rolling hash.
Search a substring of given length
that occurs at least 2 times.
@return start position if the substring exits and -1 otherwise.
"""
# compute the hash of string S[:L]
h = 0
for i in range(L):
h = (h * a + nums[i]) % modulus
# already seen hashes of strings of length L
seen = {h}
# const value to be used often : a**L % modulus
aL = pow(a, L, modulus)
for start in range(1, n - L + 1):
# compute rolling hash in O(1) time
h = (h * a - nums[start - 1] * aL + nums[start + L - 1]) % modulus
if h in seen:
return start
seen.add(h)
return -1
def longestDupSubstring(self, S: str) -> str:
n = len(S)
# convert string to array of integers
# to implement constant time slice
nums = [ord(S[i]) - ord('a') for i in range(n)]
# base value for the rolling hash function
a = 26
# modulus value for the rolling hash function to avoid overflow
modulus = 2**32
# binary search, L = repeating string length
left, right = 1, n
while left != right:
L = left + (right - left) // 2
if self.search(L, a, modulus, n, nums) != -1:
left = L + 1
else:
right = L
start = self.search(left - 1, a, modulus, n, nums)
return S[start: start + left - 1] if start != -1 else ""Java:
class Solution {
/*
Rabin-Karp with polynomial rolling hash.
Search a substring of given length
that occurs at least 2 times.
Return start position if the substring exits and -1 otherwise.
*/
public int search(int L, int a, long modulus, int n, int[] nums) {
// compute the hash of string S[:L]
long h = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < L; ++i) h = (h * a + nums[i]) % modulus;
// already seen hashes of strings of length L
HashSet<Long> seen = new HashSet();
seen.add(h);
// const value to be used often : a**L % modulus
long aL = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= L; ++i) aL = (aL * a) % modulus;
for (int start = 1; start < n - L + 1; ++start) {
// compute rolling hash in O(1) time
h = (h * a - nums[start - 1] * aL % modulus + modulus) % modulus;
h = (h + nums[start + L - 1]) % modulus;
if (seen.contains(h)) return start;
seen.add(h);
}
return -1;
}
public String longestDupSubstring(String S) {
int n = S.length();
// convert string to array of integers
// to implement constant time slice
int[] nums = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) nums[i] = (int)S.charAt(i) - (int)'a';
// base value for the rolling hash function
int a = 26;
// modulus value for the rolling hash function to avoid overflow
long modulus = (long)Math.pow(2, 32);
// binary search, L = repeating string length
int left = 1, right = n;
int L;
while (left != right) {
L = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (search(L, a, modulus, n, nums) != -1) left = L + 1;
else right = L;
}
int start = search(left - 1, a, modulus, n, nums);
return start != -1 ? S.substring(start, start + left - 1) : "";
}
}复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N \log N)$,二分查找的时间复杂度为 $O(\log N)$,$Rabin-Karp$ 字符串编码的时间复杂度为 $O(N)$。
空间复杂度:$O(N)$,用来存储字符串编码的集合。
作者:LeetCode
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-duplicate-substring/solution/zui-chang-zhong-fu-zi-chuan-by-leetcode/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。